We introduce to run and test kafka cluster in local in the first part of the Kafka Cluster series. In this post we will take a bit closer to how to use the Kafka Cluster as a middleware between different applications. Basically we will have a project which produce a message and in another project consume the message and save to database.
Introduction
Currently we have two projects as consumer and producer. These two projects communicating via Kafka. Producer produce ProductChange message and publish it to Product.change topic.
Consumer listen same topic check with product name if it hasn’t saved before then save it to product table. In current configuration we have one producer and 2 consumers.
When we will create Product.change topic, we will create it with --replication-factor 3 and --partitions as 3. So the topic will be replicated in 3 kafka brokers. And in each broker
it will has 3 partitions.
Configuration
We have 3 docker-compose.yaml files. One of them for kafka cluster, another one is for producer and last one for consumer. Kafka cluster docker-compose.yaml is same with the previous post so if you
want to check it in detail check the previous post in the first part of the Kafka Cluster series .
Producer Docker Compose Configuration
Basically producer has service configuration and networks configuration. In service configuration point out project main folder with build so docker engine know where to find
the project folder when it wants to build the image. ports, application serves in this port and in environment define the environment variables which
will be used inside producer project. In networks instead of use the default docker network we explicitly define the network name. Because we want that all docker-compose.yamls
which will be used in consumer and producer should be in same network. If you run consumer, producer and kafka cluster via same docker-compose.yaml we don’t need to define network
they will all use same network. But in our case we have to define the network name in each docker-compose.yaml file.
Another important point in producer is message key. In below code, message is created and published to kafka. ProducerRecord takes three parameters as topic name, key and value(message).
Key is important to share the load between partitions of the kafka broker. If we set the key as one constant all the messages will go to same partition and consumer can’t consume the messages in parallel.
But if it is set randomly or according to partitions count then load can shared ideally by consumers which are in same consumer group.
@Override
public void publish(String message) {
//TODO Currently randomly set the key. Better approach can be round robin with partions count.
ProducerRecord<String, String> record = new ProducerRecord<>(topicName(),
String.valueOf(message.hashCode()),
message);
kafkaProducer.send(record, produceCallback);
}
version: '3.7'
services:
spring-boot-kafka-cluster-producer:
build: ../../producer
ports:
- "12348:12348"
environment:
SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE: dev
JAVA_HEAP_SIZE_MB: 2048
ENV_KAFKA_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS: PLAINTEXT://kafka-1:19092,PLAINTEXT://kafka-2:29092,PLAINTEXT://kafka-3:39092
ENV_APPLICATION_CLIENTID: producer-1
networks:
default:
external:
name: kafka_default
Consumer Docker Compose Configuration
Consumer project is using a postgres database if you want to check its configuration in detail, you can check configure postgres section in spring boot docker post. We are running two consumers to simulate cluster environment where two nodes listen same topic and consume messages in same consumer group. This is the one of the advantage of Kafka. It is easy to provide a parallel environment and increase the throughput and reduce the latency of the applications. Because both consumers are in same consumer group they will share the partitions of the topic. If one of the consumer may stop because of some reasons(network or node crash etc.), the other one continue to consume the messages which provide availability and eventual consistency.
version: '3.7'
services:
postgres:
build: ../postgres
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: dbuser
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: password
POSTGRES_DB: store
ports:
- 5432:5432
spring-boot-kafka-cluster-consumer-1:
build: ../../consumer
ports:
- "12346:12346"
links:
- postgres
environment:
SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE: dev
JAVA_HEAP_SIZE_MB: 2048
ENV_KAFKA_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS: PLAINTEXT://kafka-1:19092,PLAINTEXT://kafka-2:29092,PLAINTEXT://kafka-3:39092
ENV_APPLICATION_PORT: 12346
ENV_APPLICATION_CLIENTID: consumer-1
spring-boot-kafka-cluster-consumer-2:
build: ../../consumer
ports:
- "12347:12347"
links:
- postgres
environment:
SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE: dev
JAVA_HEAP_SIZE_MB: 2048
ENV_KAFKA_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS: PLAINTEXT://kafka-1:19092,PLAINTEXT://kafka-2:29092,PLAINTEXT://kafka-3:39092
ENV_APPLICATION_PORT: 12347
ENV_APPLICATION_CLIENTID: consumer-2
networks:
default:
external:
name: kafka_default
How to Run
First run the kafka cluster via following command ./cleanRun-kafka.sh, if your kafka cluster doesn’t run without error please check the first post’s Kafka and Zookeeper configurations ,
be sure your kafka and zookeeper host names defined in etc/host configurations.
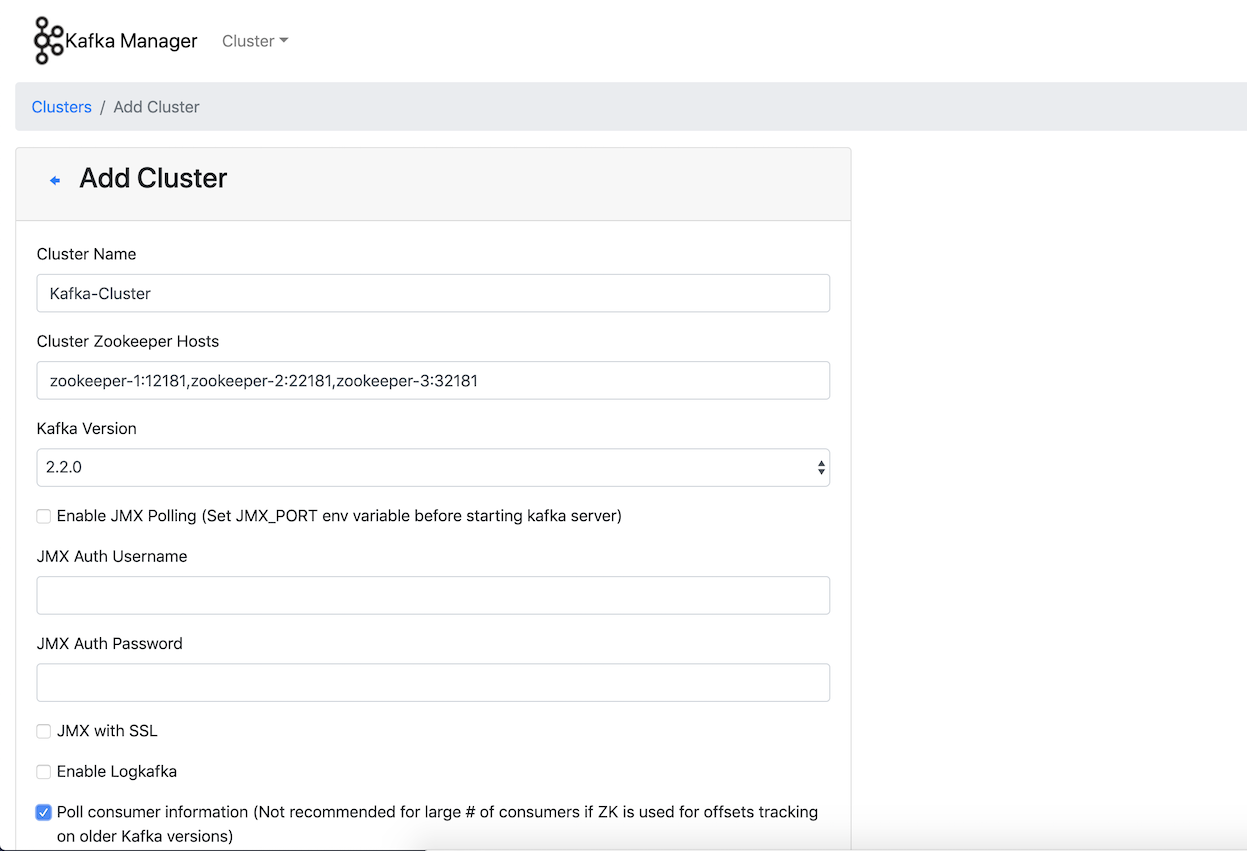
Now you can go to http://localhost:9000/addCluster to define your cluster in Kafka Manager . We define kafka-manager in
kafka-cluster docker-compose.yaml to monitor our cluster. First you have to define the cluster, zookeeper hosts and click Poll consumer information to monitor consumer group lags.
Let’s create our topic Product.change, you need a kafka client installed in your local and go to its bin directory to run ./kafka-topics.sh.
./kafka-topics.sh --create --zookeeper zookeeper-1:12181,zookeeper-2:22181,zookeeper-3:32181 --replication-factor 3 --partitions 3 --topic Product.change
Topic should be created with following message Created topic "Product.change".
Now we can run our consumer project or producer project in any order. I will run the consumer first via following command.
./cleanRun-application-consumer.sh
Then our two consumer applications will start after you saw the success logs com.softwarelabs.App : Started App in 15.794 seconds (JVM running for 17.529)
then you can also go to kafka-manager consumers page to see our consumer. http://localhost:9000/clusters/Kafka-Cluster/consumers
Now let’s start producer via following command.
./cleanRun-application-producer.sh
then you should see the success logs in starting com.softwarelabs.App : Started App in 6.077 seconds (JVM running for 7.642)
and you will see that producer starts to produce messages and consumers start to consume messages from two nodes.
Producer logs:

Consumers log:

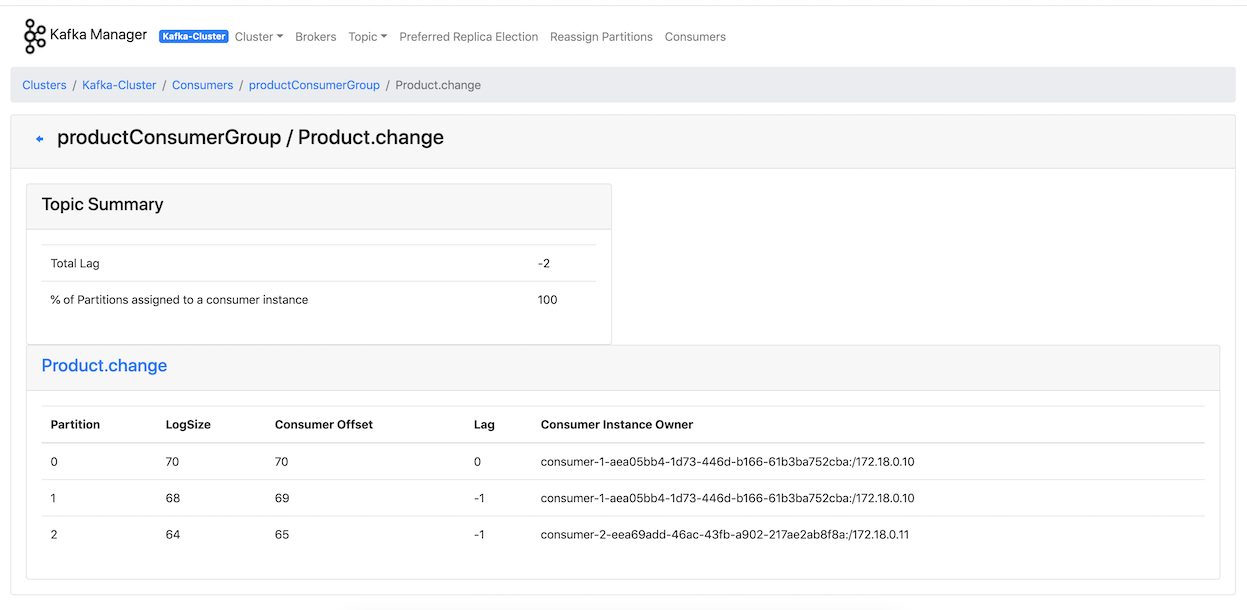
As a last step let’s revisit kafka-manager again to see that is there any lag in message consuming, if your consumers nodes run successfully it shouldn’t be.
http://localhost:9000/clusters/Kafka-Cluster/consumers/productConsumerGroup/topic/Product.change/type/KF
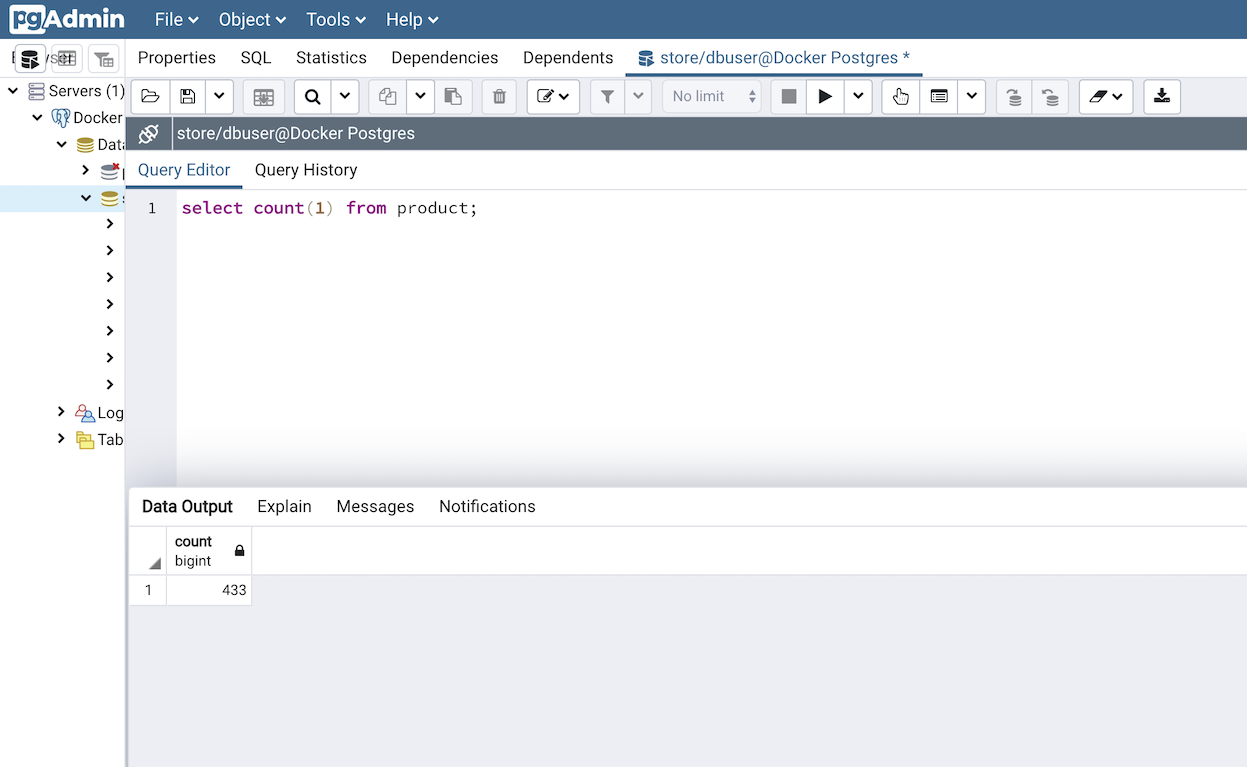
You can also see the incremental number of product records in the product table in time.
Result
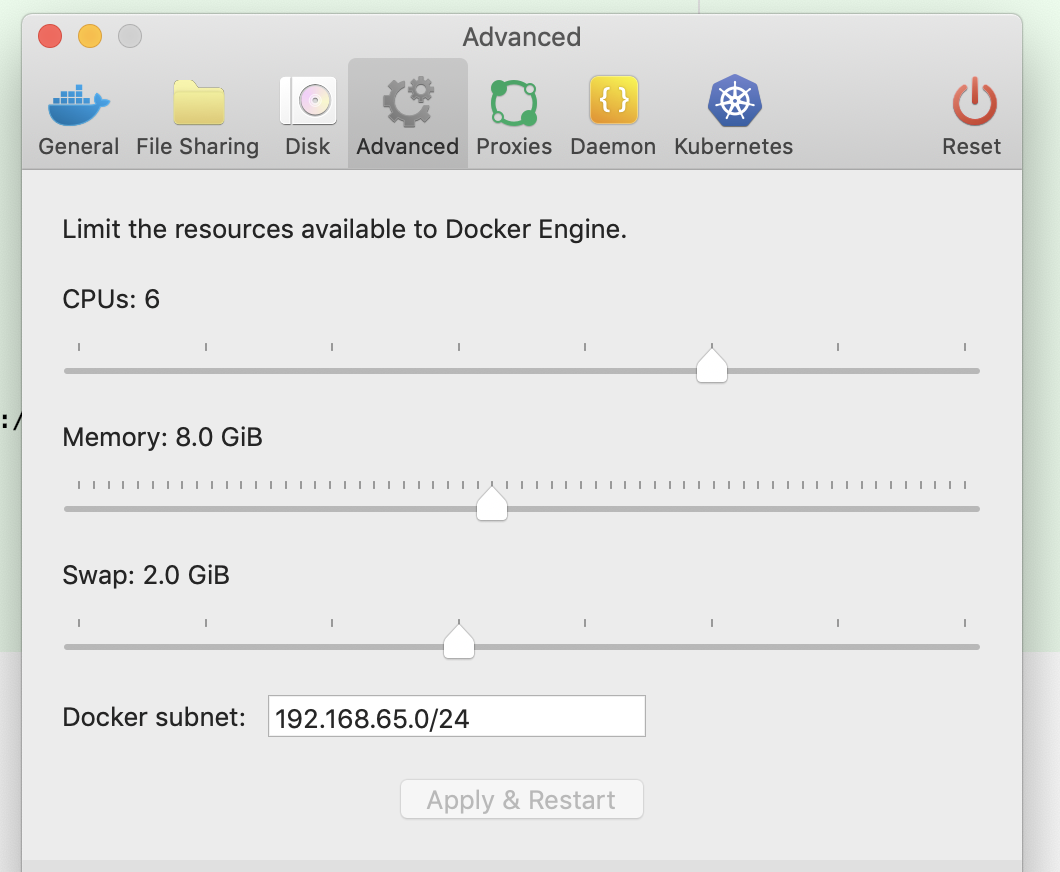
In this post we take a look how to run an kafka cluster applications in our local with docker compose. Before run this application you need to be sure that you set enough memory to docker, when docker engine memory usage was 4Gb and swap memory was 1Gb the application wasn’t run successfully in my local. I set the docker engine configuration in Docker Desktop application(version 19.03.4) via Preferences -> Advanced CPUs to 6, Memory to 8Gb and Swap to 2Gb then all the applications(kafka cluster, consumer and producer) run successfully.
You can find the all project on Github
References
https://github.com/confluentinc/cp-docker-images
https://github.com/confluentinc/examples/tree/5.1.1-post/microservices-orders
Happy coding :)